Interview with His Excellency Mr. Hassan bin Mohammed Rafei Al-Emadi, Qatar Ambassador to Japan

In this interview, the Qatari Ambassador to Japan, Mr. Hassan bin Mohammed Rafei Al-Emadi, discusses Qatar’s importance as a global economic nation, the country’s natural resources, as well as its debut hosting of the FIFA World Cup, the future of sport investment and some of the cultural highlights of the country.
Q: Please tell us about your career and how you came to be Qatar’s ambassador to Japan?

After my graduation from Cairo University in 1979, I joined the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in 1980, in which I held many positions and participated in many international conferences.
I worked as a diplomat in Islamabad from 2001 to 2003, and in Cairo from 2003 to 2005. I have served as the Ambassador to India for eight years, from 2005 to 2013, and then Ambassador to the Republic of the Union of Myanmar from 2015 to 2018. In August 2018, I assumed my current position as Ambassador to Japan.
Q: Could you describe Qatar’s recent history, including its rise to economic prominence and the current quality of life of Qataris?
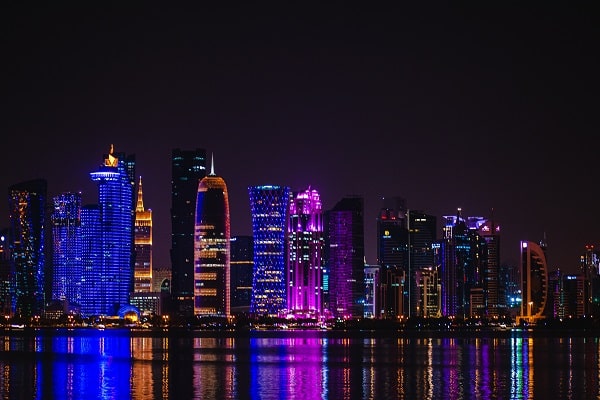
Qatar is an Arab Gulf country located on the east of the Arabian Peninsula in southwest Asia, overlooking the Arabian Gulf, and its capital is Doha. It gained its independence from Britain in 1971. The ruling Al-Thani family has been in power since the mid-nineteenth century.
Qatar is a major player in the Middle East. It is ranked as the country with the highest per capita income in the world, backed by the world’s third-largest reserves of natural gas and the thirteenth-largest proven oil reserves. The United Nations classifies Qatar as a country with very high human development, as it is one of the most advanced Arab countries in that field. The State of Qatar owns its globally expanding media group, Al Jazeera Satellite Network.

There is no income tax for the Qatari and Gulf nationals residing in the State of Qatar. The income tax in the State of Qatar is levied on the basis of an individual’s source of income, with certain exceptions. For companies, the tax rate is fixed, which is 10% of the company’s total income, and is paid annually.
Education and healthcare in Qatar are free for every citizen. Every child has the right to free education from kindergarten to high school.
The electricity and water services are free for the Qatari citizen for the first house only, and when a Qatari owns more than one house, he/she pays the service fees. The electricity price is 60% subsidized, and the resident pays 40% of the electricity price.
Q: Please elaborate on Qatar’s vast natural resources and how they are being used to support the economy?
Qatar has vast reserves of natural gas, and is one of the largest exporters of liquefied natural gas (LNG) in the world. Gas reserves in Qatar amount to 900 trillion cubic feet, making it the third-largest reserve in the world with 14.4% of the total global reserves. Qatar also possesses about 250 billion barrels of oil, which is enough for a hundred years to come.

Our wealth is being used intelligently by the sovereign wealth fund, Qatar Investment Authority, which has stepped up its business and investments around the world. The country’s energy reserves and the stable outlook of its policy reflect the extent of macroeconomic stability, and help finance the transformation of the economy under the umbrella of Qatar National Vision 2030.
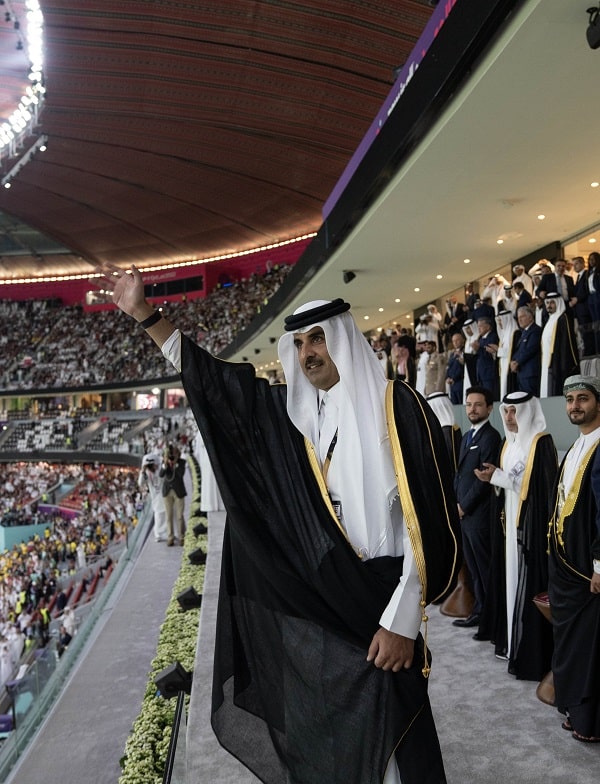
Q: This is the first FIFA World Cup to be held in Qatar, and in the Middle East. Please tell us why hosting the World Cup is so important to the country?
The World Cup is no longer just a football game for fun and entertainment — it has become a global exhibition of cultures, dialogue between peoples and civilizations, and communication between different races. The State of Qatar decided to organize this tournament for the first time in the history of world football in an Arab Muslim country and in the Middle East for the sake of correcting the misconceptions and negative stereotypes that have been attached to Arabs and Muslims for decades.

Qatar wanted to gather all the peoples of the world on Arab and Muslim lands to provide an opportunity for communication and interaction with others, to promote the principles of coexistence, tolerance, and understanding, and also to help others discover the traditions and culture of the Qatari people, introduce all elements of the Qatari identity, and introduce the Arab and Islamic civilization.
In addition to the direct economic benefits of the championship, it has indirect effects, including contributing to the development of infrastructure in the country. This is also another reason for hosting the World Cup.
Q: Qatar has spared no expense to ensure that this year’s World Cup is a profound success, with its largest-ever investment into the sport. Could you describe the facilities and equipment?
The State of Qatar’s spending on its infrastructure in the previous decade amounted to $230 billion. Most of the spending on Qatari infrastructure came within the framework of the Qatar National Vision 2030, which coincided with hosting the World Cup. In general, spending on infrastructure in Qatar, whether it is within the framework of achieving Vision 2030 or hosting the World Cup, was strategic spending. The infrastructure will continue after the end of the tournament and will be invested for decades. This supports the government’s approach to reducing dependence on oil and gas revenues in financing the state’s general budget.
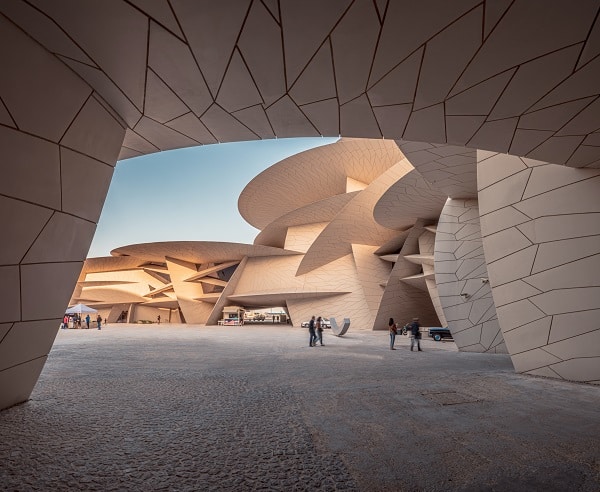

In addition to building most luxurious and modern stadiums, which will facilitate the country’s hosting of international and regional sporting events in the future, the most important projects include:
- The transportation sector by establishing and developing new and modern transportation facilities, such as the Qatar Rail Doha Metro, in addition to creating new paths for electric buses and tram systems in Lusail City and Education City;
- The expansion of Hamad International Airport to reach 50 million passengers through 1,300 daily flights;
- Other important projects include the project related to the Contribution to preserving the environment by relying on renewable energy (solar energy), building new gardens irrigated with recycled water, and replacing public buses with electric ones to reduce air pollution;
- The infrastructure related to the hospitality sector was developed as the number of hotels and resorts multiplied many times over.
In fact, the economic effects of these structures will have an impact for decades.
Q: Not only since Qatar had been granted to host the World Cup, has there been major investments in football and sports infrastructure. What kind of programs does Qatar have to continue developments in soccer beyond the World Cup?
For a country relatively new to football, Qatar has achieved several impressive footballing feats on its way to hosting the 2022 FIFA World Cup. Qatar was keen on football and bringing up promising generations by establishing the Aspire Academy in 2004 to provide sports training, rehabilitation, and education for athletically gifted students in Qatar during their academic career.
Aspire succeeded in providing the national team with players who changed the map of Qatari football, on the continent and the world. Over the past years, the Academy has produced a generation of talented players who added a new dimension to Qatari football, and engraved their names in golden letters in its history. Aspire’s graduates were the main strength of the Qatar team that won the Asian Junior Championships in 2014, and the Qatar national team was able to win the gold medal in the 2006 Asian Games held in Doha. In addition, 15 graduates participated in the squad that was crowned with the 2019 Asian Nations title, and there are 19 players in the squad who competed in the Qatar World Cup 2022 Finals.
Q: Are there any plans for Qatar to host the Olympic Games in the future?
After the great success achieved by the State of Qatar in hosting the FIFA World Cup Qatar 2022, our determination to host the 2036 Olympic Games in Doha has become stronger. We also plan to host many prestigious sports competitions in the future.
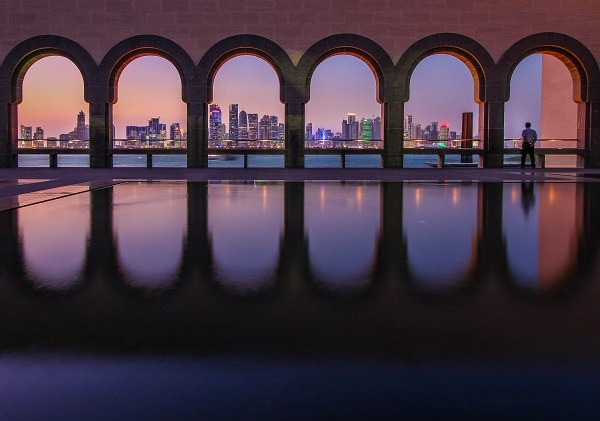
Q: Qatar has some wonderful cultural institutions, including the Qatar National Museum and the modern architecture in Doha. Can you describe some of the aspects of tourism, food and culture in Qatar?
The State of Qatar makes tourism a priority, and aspires to be a preferred destination for tourists in the world in the near future. Over the past two decades, the State of Qatar has sought to diversify its domestic tourism destinations. The revival of the heritage Souq Waqif, the establishment of the cultural neighborhood (Katara), and finally the opening of the Qatar National Museum were the biggest testaments to the state’s keenness on the cultural aspect of tourism.
Qatar also sought to interest nature lovers by opening the way for camping in the desert. Shopping tourism has also found a prominent place in Qatar during the last period, especially with its eagerness to hold the Qatar Shopping Festival annually as well as many festivals and events aimed at promoting tourism in the country, along with the presence of dozens of major shopping malls that support this field.

Qatar National Museum is considered the most prominent cultural landmark in the State of Qatar, as it combines comprehensive architectural design between tradition and modernity.
As for Pearl Island, it is the most beautiful and finest tourist attraction in Qatar, consisting of many artificial islands.
Katara, in addition to being a destination for tourism in the country, it is a cultural hub that aims to promote the cultural movement in Qatar. It is a meeting place for all intellectuals and artists, and a center for promoting cultural awareness through festivals, exhibitions, seminars, and concerts.
Qatar’s rich culture and heritage, the hospitality of the Qatari people, and the availability of delicious international cuisine and restaurants from all over the world are also an attractive factor for tourists.
We thank Ambassador Al-Emadi for the interview.
Read more: